| General Example |
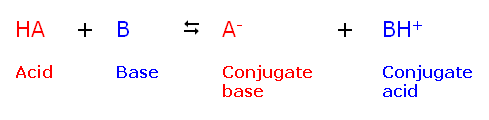 |
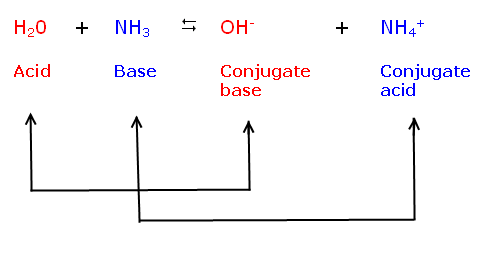
| Specific Example |
 |
BIOL 1406
PreLab 3.2
What are acids and bases?
Although several definitions for acids and bases exist, in this class we will
define an acid as a proton donor, and a base as a proton acceptor. Remember, a
proton is just another name for a hydrogen ion (H+). When an acid donates a
proton to a base, the acid becomes a conjugate base (since it is now a proton
acceptor) and the base becomes a conjugate acid (since it is now a proton
donor):
| General Example |
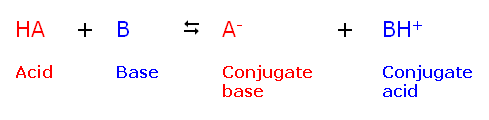 |
| Specific Example |
 |
Because acids are proton donors, they act to increase [H+] when dissolved in
water. For example, when hydrochloric acid (HCl) is dissolved in water, it
dissociates to form H+ and Cl- . The release of H+ ions increases [H+] in the
solution. Also, remember that in any aqueous solution as [H+] increases [OH-]
will decrease.
On the other hand, because bases are proton acceptors they act to decrease the
[H+] when dissolved in water. Bases can decrease the [H+] in two ways:
In sum, when an acid is added to an aqueous solution, [H+] increases and [OH-]
decreases. When a base is added to an aqueous solution, [OH-] increases and [H+]
decreases.
Acids and bases can vary in the extent to which they alter [H+] and [OH-].
Strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4), almost
completely dissociate in water. Therefore, they produce a relatively large
increase in [H+] and a correspondingly large decrease in [OH-]. On the other
hand, weak acids, such as acetic acid and citric acid, have a much lower level
of dissociation. Therefore, they produce a relatively small increase in [H+] and
a correspondingly small decrease in [OH-]. Similarly, strong bases, such as
sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH), produce a large increase
in [OH-] when dissolved in water, while weak bases such as ammonia (NH3) and Trizma® base produce a much smaller increase in [OH-]. Most biomolecules have
properties of weak acids and/or bases.
| YOUR TURN | ||
A hydrogen ion is another name for a |
Hint | Check your answer. |
| When an acid is added to an aqueous solution, increases and decreases. | Hint | Check your answer. |
| When a base is added to an aqueous solution, increases and decreases. | Hint | Check your answer. |
Close this browser window to return to Blackboard and complete the practice quiz and assessment quiz.