Explain why:
Explain why:
BIOL 1406
PreLab 5.2
How do substances move across a selectively permeable membrane?
A selectively permeable membrane is a membrane that allows some substances to pass through easily, while other substances pass through very slowly or not at all. All cell membranes, including the plasma membrane, are selectively permeable. In the exercise below, you will learn about 2 types of diffusion across selectively permeable membranes:
|
Use the interactive exercise below to learn more about simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. |
| Your Turn | ||
| Assume there is a higher concentration of each of the following substances in the extracellular fluid surrounding a cell than in the cellís cytoplasm. Predict whether the substance would be more likely to enter the cell by simple diffusion or by facilitated diffusion, and explain why. | ||
| Is O2 more likely to enter the
cell by
simple diffusion or facilitated diffusion:
Explain why: |
Hint | Check your answer. |
| Is glucose more likely to enter the cell by simple
diffusion or facilitated diffusion:
Explain why: |
Hint | Check your answer. |
| Is Na+ more likely to enter the
cell by
simple diffusion or facilitated diffusion:
Explain why: |
Hint | Check your answer. |
| Is insulin (a protein) more likely to
enter the cell by simple diffusion or facilitated diffusion:
Explain why: |
Hint | Check your answer. |
| Is estrogen (a lipid) more likely to enter
the cell
by simple diffusion or facilitated diffusion:
Explain why: |
Hint | Check your answer. |
| Are hydrogen ions more likely to enter the
cell by
simple diffusion or facilitated diffusion:
Explain why: |
Hint | Check your answer. |
Dialysis tubing is composed of a selectively permeable membrane. However,
its selectivity is much more limited than the selectivity of cell membranes.
Microscopic holes, or pores, in the dialysis tubing allow substances to be
separated only on the basis of size. Unlike with cell membranes, whether the
substance is nonpolar, polar, or charged has little effect on its ability to
cross the tubing. Molecules and ions that are smaller than the pores can move
through the tubing, while those that are larger than the pores cannot. Dialysis
tubing can be ordered from scientific supply companies in a variety of pore
sizes. Dialysis is routinely used in biochemistry and molecular biology
laboratories to separate and purify substances on the basis of size.
| Your Turn | ||
| Of the substances listed in the exercise above (O2, glucose, Na+, insulin, estrogen, and hydrogen ions) which would not pass easily through the plasma membrane by simple diffusion, but probably would pass through the pores of dialysis tubing? (Hint: There are 2 correct answers.) | ||
| List the substances: | Hint | Check your answer. |
| Explain why: | Hint | Check your answer. |
Diffusion of materials through cell membranes always involves net movement of a
substance down its own concentration gradient (from higher concentration to
lower concentration.) However, in some cases substances must be transported
across cell membranes against their concentration gradient (from lower
concentration to higher concentration.) This requires cellular energy and,
therefore, a form of active transport. For example, the transfer of a phosphate
group from an ATP molecule to a membrane protein may change the shape of the
protein, causing it to pump a substance across the membrane against its
concentration gradient. Whenever a substance is being moved against its
concentration gradient, a form of active transport is required.
| Your Turn | ||
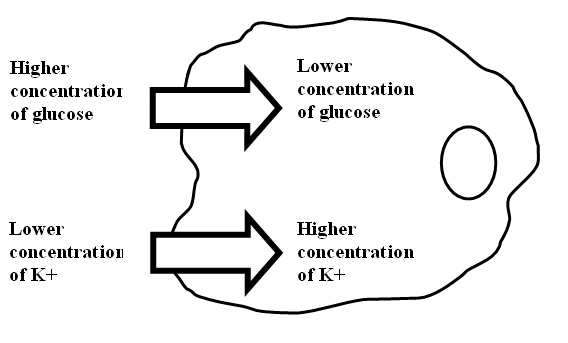
| Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport allow the cell to be very selective about what is allowed to cross its membranes. Examine the figure below, and answer the questions. | ||
 |
||
| Will glucose enter the cell by simple
diffusion, facilitated diffusion, or active transport?
Explain why: |
Hint | Check your answer. |
| Will K+ enter the cell by simple
diffusion, facilitated diffusion, or active transport?
Explain why: |
Hint | Check your answer. |
Close this browser window to return
to Blackboard and complete the practice quiz and assessment quiz.