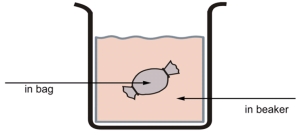
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. isotonic B. hypotonic C. hypertonic
A. isotonic B. hypotonic C. hypertonic
A. from the hypertonic solution to the hypotonic solution
B. from the hypotonic solution to the hypertonic solution
C. both directions
D. neither direction
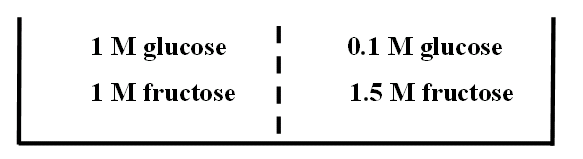
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. left to right B. right to left C. both directions D. neither direction
A. isotonic B. hypotonic C. hypertonic
A. isotonic B. hypotonic C. hypertonic